Sodium FENa Calculator - Acute Kidney Injury
"Determine cause of renal failure based on fractional excretion of sodium (FENa)"
Download now:
"Sodium FENa Calculator - Acute Kidney Injury" is a mobile app designed to help health practitioner to calculate the fractional excretion of sodium (FENa). This FENa score in "Sodium FENa Calculator - Acute Kidney Injury" app can be used to determine if acute renal failure or acute kidney injury (AKI) is due to pre-renal, renal, or post-renal pathology. The result of calculation will assist in management of patient with acute kidney injury or renal failure.
There are several features of "Sodium FENa Calculator - Acute Kidney Injury", namely:
🔸 Simple and very easy to use FENa calculator.
🔸 Precise calculation of fractional excretion of sodium (FENa).
🔸 Calculation of FENa based on serum creatinine, urinary creatinine, serum sodium, & urinary sodium
🔸 Determine the cause of acute kidney injury (pre-renal, renal, or post-renal pathology)
🔸 It is totally free. Download now!
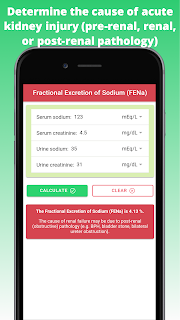
Fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) score <1% is associated with pre-renal pathology, for example hypovolemia, heart failure, renal artery stenosis, or sepsis (anything causing decreased effective renal perfusion). Fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) score >4% is associated with post-renal pathology or obstruction, for example bladder prostate hyperplasia (BPH), bladder stone, bilateral ureter obstruction. While fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) score between 1-4% is associated with intrinsic pathology (for example acute tubular necrosis (ATN), acute interstitial nephritis (AIN), or glomerulonephritis). Fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) score is calculated from 4 parameters, namely serum creatinine, urinary creatinine, serum sodium, and urinary sodium.
Disclaimer: all calculations must be re-checked and should not be used alone to guide patient care, nor should they substitute for clinical judgment. Calculations in "Sodium FENa Calculator - Acute Kidney Injury" app might be different with your local practice. Consult to expert doctor whenever necessary.














0 comments:
Post a Comment